1) Degrees and Radians
2) Circle Central Angle
3) Quadrant and Semicircle
4) Angles and Chords
There are quite a few different situations where specific angles in a circle can crop up.
It’s handy know some of the common properties of these angles seeing as the circle is one of the most common shapes to encounter in Math.
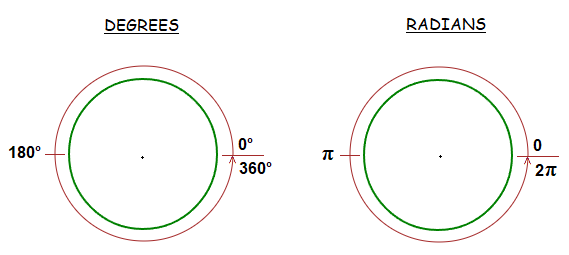
Degrees and Radians
With regards to degree measure, there is 360° in a full size circle.
But added to degrees, there is also radian measure, with which there are 2π radians in a full size circle.
The angles in a circle can be measured with both degree and radian measure.
This page will display examples of angles measured with degrees.
Further information on radian measure can be viewed here.
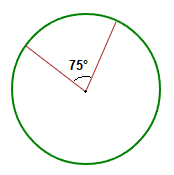
Central Angle of a Circle
The central angle of a circle is an angle formed by 2 radius lines, connected together by a vertex at the center point of the circle.
The circle below has a central angle of size 75°.
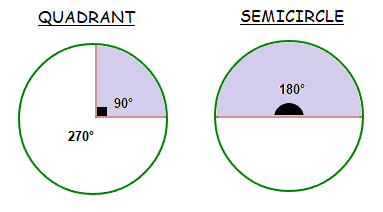
Circle Quadrant and Semicircle
In a standard circle, a quadrant is the size of one quarter or one fourth of the circle.
The angle that is inside a quadrant is 90°, which results in the angle outside the quadrant in the circle being 270°.
A semicircle is half a circle, and is thus the size of 2 quadrants together. So the size of the angle inside a semicircle is 180°, as is also the angle outside of the semicircle.
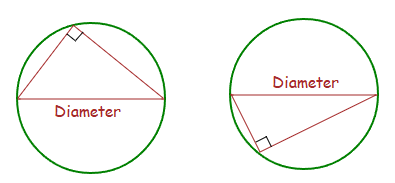
Triangles in a Semicircle
If you have a triangle inside a semicircle, it will always be a right angle triangle, with the angle NOT alongside the diameter being 90°.
Angles and Chords in a Circle, Inscribed Angle
An angle that is inscribed by 2 chords in a circle, will have a vertex that is on the circle circumference.
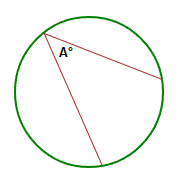
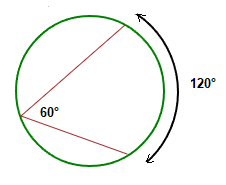
The size of the inscribed angle, is half of the size of the arc formed by the other ends of the 2 circle chord lines.
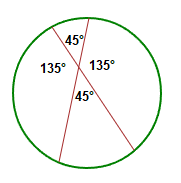
Angles in a Circle between intersecting Chords
Four angles are formed when 2 chord lines inside a circle intersect each other.
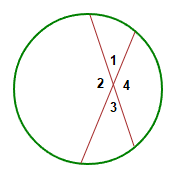
These four angles are in fact 2 pairs of angles that are vertically opposite to each other.
Which means:∠1 = ∠3 AND ∠2 = ∠4
We can see this with actual angle measurements in another illustration below.